Optimizing Application Performance: Harnessing the Power of Load Balancing and Auto Scaling on AWS
Table of contents
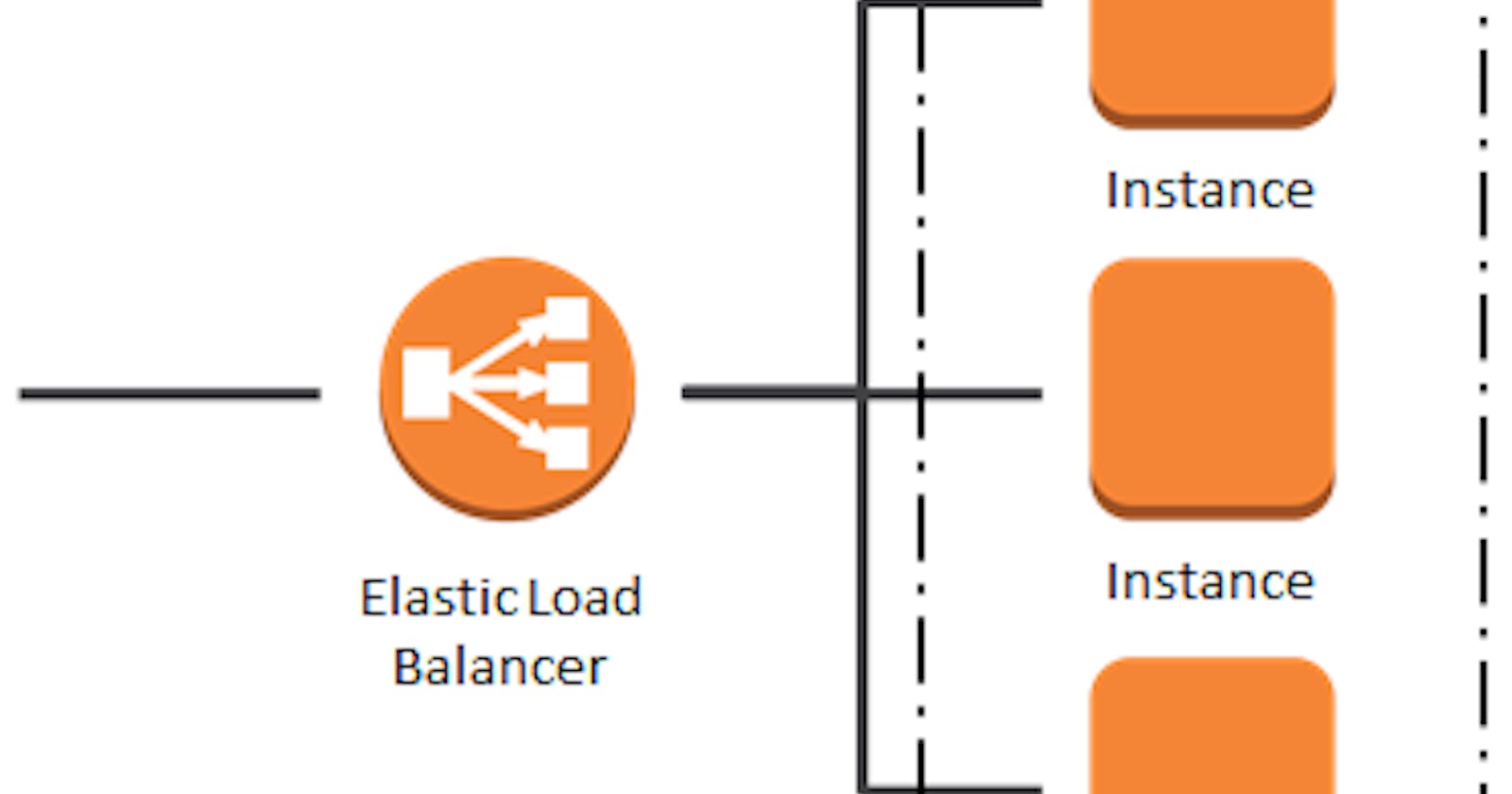
What is a Load Balancer?
- A load balancer is a networking device or service that evenly distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers or backend instances.
Key Features:
⚖️ Load Distribution: Balances traffic load among servers to prevent overload and ensure efficient resource utilization.
🔄 Health Checks: Regularly monitors server health and redirects traffic away from unhealthy instances.
🔒 SSL Termination: Offloads SSL decryption to improve performance and security.
🚦 Traffic Routing: Supports various routing algorithms like Round Robin, Least Connection, and IP Hash.
🏗️ Creating Load Balancer and Attaching EC2 Instances:
Navigate to Load Balancer Console:
- Access the AWS Management Console and navigate to the Load Balancer section.
Create Load Balancer:
- Follow the prompts to create a new load balancer, specifying details like load balancer type (e.g., Application Load Balancer, Network Load Balancer), listeners, and availability zones.
Configure Target Groups:
- Create target groups and define the criteria for routing traffic to registered instances (e.g., EC2 instances).
Register EC2 Instances:
- Register the desired EC2 instances with the target groups to enable the load balancer to distribute incoming traffic to them.
Adjust Load Balancer Settings:
- Fine-tune load balancer settings as needed, such as health checks, stickiness, and connection draining.
🚀 Experience the Load Balancer:
Testing Traffic Distribution:
- Send test traffic to the load balancer endpoint and observe how it distributes requests among the registered instances.
Monitoring Performance:
- Monitor load balancer metrics, such as request counts, latency, and backend server health, to ensure optimal performance.
🛠️ Simulating Failure Scenario:
Triggering Failure Conditions:
- Simulate failure scenarios by intentionally stopping instances, removing them from the load balancer, or introducing network issues.
Observing Load Balancer Response:
- Observe how the load balancer dynamically adjusts to failures by rerouting traffic away from unhealthy instances and maintaining service availability.
What is Auto Scaling?
Definition:
- Auto Scaling is a feature of AWS that automatically adjusts the number of EC2 instances in a group based on predefined conditions and metrics.
Key Benefits:
⚖️ Efficient Resource Management: Ensures that you have the right number of instances to handle varying levels of traffic.
🌟 Improved Reliability: Enhances application availability by automatically replacing unhealthy instances.
💰 Cost Optimization: Helps optimize costs by scaling resources up during peak demand and down during periods of low utilization.
🚀 Understanding Launch Configuration:
Definition:
- A launch configuration defines the settings for newly launched instances, including the AMI (Amazon Machine Image), instance type, security groups, and key pair.
Key Components:
🖥️ AMI: Specifies the base operating system and software configuration for instances.
🛠️ Instance Type: Determines the computing resources allocated to instances, such as CPU, memory, and network performance.
🔒 Security Groups: Controls inbound and outbound traffic to instances.
🔑 Key Pair: Provides secure access to instances via SSH or RDP.
🎯 Understanding Auto Scaling Group:
Definition:
- An Auto Scaling group is a logical grouping of EC2 instances that share similar characteristics and are managed collectively.
Key Features:
🔄 Scaling Policies: Define rules and conditions for scaling actions, such as scaling out (adding instances) or scaling in (removing instances).
📊 Scaling Metrics: Monitor metrics like CPU utilization, network traffic, and custom metrics to trigger scaling events.
🚥 Lifecycle Hooks: Enable custom actions to be performed before instances are launched or terminated.
📩 Creating Notifications (SNS Service):
Notification Service (SNS):
- SNS is a fully managed pub/sub messaging service that enables you to send notifications to a variety of endpoints, including email, SMS, HTTP, and AWS Lambda functions.
Integration with Auto Scaling:
- Configure SNS topics to receive notifications about Auto Scaling events, such as instance launches, terminations, and scaling actions.
🚨 Creating Alarms (CloudWatch Service):
CloudWatch Alarms:
CloudWatch is a monitoring and observability service that collects and tracks metrics, logs, and events.
Create alarms based on CloudWatch metrics to trigger Auto Scaling actions when predefined thresholds are breached.
➕ Adding Auto Scaling Policies:
Scaling Policies:
Define scaling policies to specify how Auto Scaling should respond to changes in demand or system metrics.
Configure policies to scale out by adding instances when demand increases or scale in by removing instances during periods of low utilization.
🛡️ What is AWS WAF?
Definition:
- AWS WAF is a web application firewall that helps protect your web applications from malicious attacks and unwanted traffic.
Key Features:
🚫 Protection Against Common Threats: Shields against common web security threats such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and HTTP floods.
🔍 Granular Control: Allows you to define customizable rules to filter and block specific types of traffic based on criteria such as IP addresses, HTTP headers, and request methods.
🔄 Dynamic Updates: Provides regular updates and rule sets maintained by AWS and third-party security experts to adapt to evolving threats.
🚀 Getting Started with AWS WAF:
Navigate to AWS WAF Console:
- Access the AWS Management Console and navigate to the AWS WAF service.
Create a Web ACL (Access Control List):
- Define a Web ACL to specify the rules and conditions for filtering incoming traffic to your web applications.
Configure Rules and Conditions:
- Set up rules to inspect and filter incoming requests based on criteria such as IP addresses, HTTP headers, query strings, and request methods.
Associate Web ACL with Resources:
- Associate your Web ACL with the resources (e.g., Amazon CloudFront distributions, Application Load Balancers, Amazon API Gateway APIs) that you want to protect.
🔒 Enhancing Security with AWS WAF:
Protecting Against OWASP Top 10 Threats:
- Leverage AWS Managed Rules for AWS WAF to automatically protect against the OWASP Top 10 web application security risks.
Customizing Rules and Conditions:
- Tailor AWS WAF rules to match the specific security requirements and attack patterns of your web applications.
📈 Monitoring and Insights:
Real-Time Monitoring:
- Monitor traffic patterns and security events in real-time using AWS CloudWatch Logs and metrics.
Insights and Reporting:
- Gain insights into potential security threats and vulnerabilities through detailed logging and reporting features provided by AWS WAF.
💼 Use Cases and Benefits:
Protecting Web Applications:
- Safeguard your web applications from common security threats and attacks, ensuring their availability and integrity.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements:
- Meet compliance requirements and industry standards by implementing robust security measures with AWS WAF.
Cost-Effective Security:
- Achieve cost savings by leveraging AWS WAF's pay-as-you-go pricing model and eliminating the need for costly on-premises security solutions.